Watch CBS News
Be the first to know
Get browser notifications for breaking news, live events, and exclusive reporting.
Watch CBS News
Be the first to know
Get browser notifications for breaking news, live events, and exclusive reporting.
Watch CBS News
Be the first to know
Get browser notifications for breaking news, live events, and exclusive reporting.
The following is a transcript of an interview with Cindy McCain, World Food Programme executive director, that aired on March 31, 2024.
ED O’KEEFE: We’re joined by the Executive Director of the World Food Program, Cindy McCain. Mrs. McCain, it’s great to see you. Thank you for joining us. Simply put–
EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR WORLD FOOD PROGRAM, CINDY MCCAIN: My pleasure.
ED O’KEEFE: Simply put, right now there are too many people in the world going hungry and you have some critical insights into that, which is why we’re so pleased that you’re with us this morning. I wanted to begin with the situation earning the most attention right now in Gaza and as the war continues, the International Court of Justice this week called for Israel to, quote “take all necessary and effective measures” to allow humanitarian assistance into Gaza. What needs to change so that your teams can operate there?
CINDY MCCAIN: Well, first of all, thank you for covering this issue. We need access. We need full, unfettered access and right now we don’t have that. We can occasionally get a few trucks in. We can occasionally get up all the way to the north, but it’s not consistent and is- and is not to scale either. All of the other issues regarding maritime and airdrops and all those are all good. We need any- any way to be able to get food in- in any way we can, but they can’t take it to scale. We really need access to the road and we need to be able to get up to the north, all the way without being caught at checkpoints and turned around.
ED O’KEEFE: I read the World Food Program estimates simply addressing the basic food needs will require at least 300 trucks to enter Gaza every day and distribute food, especially in the north, as you mentioned, but you’ve only managed to get about nine convoys of trucks in since the start of the year. That’s nothing, right?
CINDY MCCAIN: It’s nothing. It really is. We were able to yesterday, or today I guess it was, get nine trucks in, period. We also were part of an airdrop today that was 6.1 metric tons. That’s nothing. We just cannot continue this way. As you know, famine is imminent in the north and so unless we can- can really convince our- our diplomatic groups and our political groups around the world to help convince the Israelis that we must get in and we must do it in a- in a sustained and unfettered- unfettered way. We can’t- people are going to die otherwise, and they already are dying.
ED O’KEEFE: When you or your colleagues speak with Israeli officials about getting that access, what is the reason they’re giving you why they’re not letting you in? Do they not understand the situation? Or is there some other reason?
CINDY MCCAIN: Well, I’m not really sure where the mistake has been made, but I do know that there’s been accusations that somehow the U.N. isn’t doing their job, which couldn’t be further from the truth. So I think again, it’s politics. I think it’s something that- that we’re, you know, various factions are involved in, all I want, all I need to know is when and where we can take the food in, make sure that we can distribute it. That’s what I want to know from the Israeli government.
ED O’KEEFE: You’re especially concerned as well about what’s happening in parts of Africa, specifically Sudan, South Sudan, and Chad, and you said, this could become the world’s largest hunger crisis. Why is that?
CINDY MCCAIN: Well, quite frankly, it’s the forgotten crisis now. Sudan no- is no longer paid attention to in the world media, and- and things haven’t stopped there. People are still fighting, there is no food. We have no access and we’re also fighting a climate change issue there as well. So it’s almost a combination of a perfect storm, with- with 2.2 million refugees across the borders, in various countries, especially Chad and the funding sources that we have right now and our ability to be able to fund, it just isn’t- isn’t meshing. We don’t have enough money and we need to be able to make sure that we can feed the refugees that are across the border, and also get access into Sudan from this- from- from the- the western side, the southern side, through South Sudan, and through the north, we’ve got to get food in there as well, because it can be and will be, I hope not, I pray not, the next- the next largest humanitarian crisis that will- that we will know.
ED O’KEEFE: And not only humanitarian crisis, you’ve suggested it could be a real national security risk for the United States, right?
CINDY MCCAIN: Very much so. People migrate, you know, the bad guys get mixed up in all of this. Food is the- is the major element here in being able to keep populations stable and keep- keep them healthy as well. With those two things not tended to, then people migrate, they run, they take their families, they do anything they can to feed their families.
ED O’KEEFE: You’ve made an interesting point that I think is a good reminder to all of us that these hunger crises around the world are not being caused by natural disasters, but by man-made events and conflict. And nowhere right now, perhaps, at least in this hemisphere, where we sit, is that most apparent than in Haiti, what is the situation there, as you understand it?
CINDY MCCAIN: It’s catastrophic. We- we WFP are still in there and we still are working in the north somewhat and somewhat down towards the center, but it is a very dicey situation. We are continuing our school feeding programs, but once again, as you’ve seen, there have been evacuations of U.N. personnel out of there. It’s just, again, this is a diplomatic solution. This is a man-made crisis, and we need a diplomatic solution to it and we need it now. We need it right now.
ED O’KEEFE: You know, we’d be remiss if we didn’t ask you while we have you about the death of the late Senator Joe Lieberman, who of course, was such a good friend to you and to your late husband, what did he mean to the McCain family?
CINDY MCCAIN: Oh, he was Uncle Joe to my children, he was a friend to my family and- and I had the extreme opportunity of watching two men together, not only navigate the difficulties that the world offered up to them as- as in what they did, but also watch them solve problems together in a way that was gracious and kind and loving towards humanity. And I had the good fortune of being able to call him my friend too.
ED O’KEEFE: Executive Director, Cindy McCain of the World Food Program, thank you for joining us.
CINDY MCCAIN: Thank you for having me.
ED O’KEEFE: And we’ll be right back.
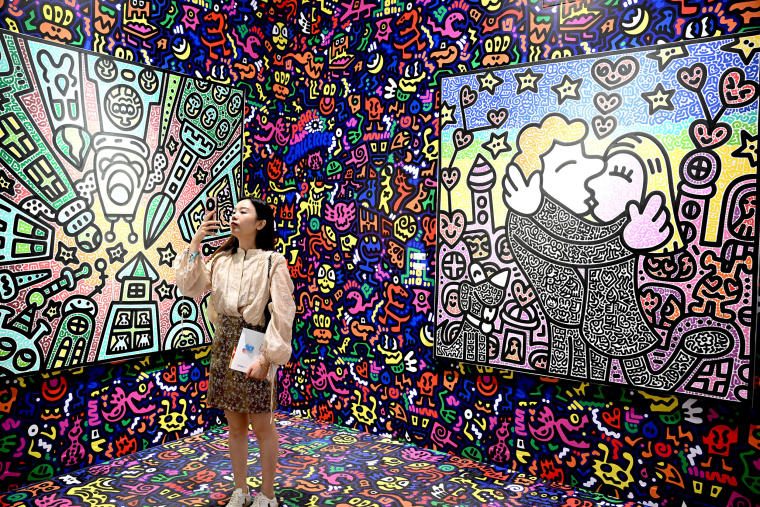
More than 240 international galleries are participating in Art Basel this year, as it returns to full scale for the first time since before the pandemic. A related Art Week event, Art Central, features almost 100 galleries from Hong Kong and around the world.
The two events have been thronged with people this week, both serious art buyers as well as casual ticketholders snapping photos and selfies.
The government provided Art Basel with 15 million Hong Kong dollars ($1.9 million) from a fund aimed at promoting major arts and cultural events, which supported Art Central as well. Officials see such “mega events” as a way to revive Hong Kong’s economy and its international reputation, which has been battered by years of pandemic isolation and the crackdown on dissent.
Hong Kong Culture Secretary Kevin Yeung told lawmakers on Wednesday that the government was “committed to promoting Hong Kong as an East-meets-West center for international cultural exchange,” citing the city’s low tax rate and strategic location in Asia.
Art Basel has played down concerns about free expression.
“We have never faced any censorship issues at our shows, nor have we been asked to do anything differently since the introduction of the National Security Law,” a spokesperson said in a statement. “As with all Art Basel shows, our Selection Committee is responsible for reviewing applications and selects galleries solely based on the quality of their booth proposal.”
But that obscures the self-censorship that galleries may now feel is necessary to be included in major art fairs, said Wear, who published a statement last year urging the international artistic community not to participate in Art Basel’s Hong Kong event.
“They don’t have to do it because everybody does it for them,” he said.
The Hong Kong government has been investing heavily in the city as a cultural hub, opening the M+ art museum in 2021 and the Hong Kong Palace Museum in 2022. And the world’s biggest auction houses continue to express confidence: Phillips opened its new Asia headquarters in Hong Kong in 2023, to be followed by Christie’s and Sotheby’s later this year.
But Hong Kong’s cultural development has coincided with a crackdown on dissent in the name of national security, raising difficult questions for international art companies that don’t want to miss out on commercial opportunities.
“They know they have a problem, but they don’t want to talk about it,” said Danish sculptor Jens Galschiot. “Because the moment they talk about it, then they must face it.”
In 2021, a sculpture by Galschiot memorializing the victims of the 1989 Tiananmen Square crackdown on pro-democracy protesters in Beijing was dismantled and removed from the University of Hong Kong, where it had stood since 1998. University officials said they removed the sculpture, called the “Pillar of Shame,” “based on external legal advice and risk assessment.”
Hong Kong officials have made it no secret that art could be targeted. The city’s security chief, Chris Tang, said in a letter to Galschiot last year that those seeking to endanger national security could use “artistic creations” as a pretext.
Alexandra Yung, a local artist, art collector and art consultant, said there was a feeling of “apprehension” among Hong Kong’s artistic community, some members of which have moved abroad. Artists now have to be “a bit more aware and more responsible,” she said, amid uncertainty over where the “red lines” are drawn.
While in past years Hong Kong’s Art Week events have featured art related to local politics, Yung said this year she “didn’t see anything that was political at all.”
“I think galleries are more aware of what they would show and what they wouldn’t show,” she said.
Hong Kong was required to pass the Article 23 law under its mini-constitution, known as the Basic Law, but a previous attempt was aborted in 2003 when an estimated 500,000 of Hong Kong’s 7.5 million people took to the streets in protest. Since the national security law was imposed in 2020, however, Hong Kong’s pro-democracy opposition has been all but wiped out, and this time the bill sailed through the legislature, where it passed unanimously on March 19.
The law has been criticized by the United States and others, with Secretary of State Antony Blinken saying it “threatens to further undermine the rights and freedoms of people in Hong Kong.”
The Hong Kong government condemned Blinken’s remarks as “misleading and erroneous,” saying the law is precisely targeted, its crimes and penalties are clearly defined and established freedoms will be protected.

Among the aspects of the new local law of greatest concern to artists is sedition, a British colonial-era crime that Hong Kong officials have resurrected in recent years, said Eric Yan-ho Lai, a research fellow at the Georgetown Center for Asian Law.
The new law expands the crime of sedition, defined as inciting hatred or disaffection toward the Chinese and Hong Kong governments, and raises the maximum punishment from two years in prison to 10.
“There’s already strong self-censorship in Hong Kong in the past few years,” Lai said, pointing to the removal of politically sensitive books from public libraries and schools.
During last year’s Hong Kong Art Week, a video installation by an American artist was removed from a billboard outside a department store after it was discovered to be secretly paying tribute to the 2019 protesters, more than 10,000 of whom have been arrested.
In August, a longstanding mural was removed from outside a restaurant popular with construction workers because it depicted patrons eating noodles while wearing yellow hard hats, a color associated with pro-democracy protesters.
In recent months, national security considerations have also seemingly played a role in the cancellation of multiple performances. In January, organizers of the Hong Kong Drama Awards said they had been told that the government-funded Hong Kong Arts Development Council was withdrawing support for the first time in more than two decades out of concern for its reputation.
Among the reasons the council cited was the invitation of “non-theatrical people” as presenters at last year’s awards, including the controversial political cartoonist known as Zunzi.

Lai said the heightened legal risk brought by the Article 23 law would worsen self-censorship, which in turn would “make Hong Kong become less vibrant and pluralistic and further discourage artistic communities from abroad to visit Hong Kong.”
The effects of self-censorship could also ripple out from Hong Kong to the wider world, Wear said, noting that Western galleries and other arts organizations have rarely contended with restrictive laws of this kind in an art market as big as Hong Kong’s. Like Beijing’s national security law, the Article 23 law claims global jurisdiction.
“If you’re a dealer bringing work, say, to Art Basel, or if you have an operation in Hong Kong, you may hesitate about having work anywhere in your system that might upset the Hong Kong or Chinese authorities,” said Wear, who was associate head of the School of Design at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University from 1989 to 2006.
Galschiot said it was the responsibility of Western arts organizations and auction houses to speak out on behalf of a Hong Kong artistic community that has been “castrated” by the national security laws.
“They must take the fight now from the artists,” said Galschiot, whose sculpture was reportedly seized from storage by Hong Kong national security police last year in connection with an “incitement to subversion” case.
Hong Kong officials declined last year to confirm or deny reports that there was a warrant out for Galschiot’s arrest.
Wear said Hong Kong is unlikely to lose its prominent position in the art world any time soon.
“The art market is very likely to persist, and very possibly even likely to grow,” he said. “It’s just that a lot of things won’t be possible.”
(Bloomberg) — Eskom Holdings SOC Ltd., South Africa’s state power company, disputed the findings of a Greenpeace report that it operates many of the world’s worst emission sites for toxic nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide.
Most Read from Bloomberg
The Major Air Polluters in Africa report, released Thursday by Greenpeace in collaboration with the Centre For Research on Energy and Clean Air, asserted that coal-fired plants operated by the utility account for five of the world’s 10 biggest single-source nitrogen-dioxide emission sites. The company also runs two of the 10 worst sulfur-dioxide sites, Greenpeace and CREA said.
“The Greenpeace report appears to rely on satellite interpretation of the high levels of nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide in the troposphere,” Eskom said in a response to queries. It “links the nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide measured many hundreds of meters above the ground to direct health impacts at ground level,” the utility added.
South Africa, which relies on coal for the generation of more than 80% of its electricity, has some of the world’s worst air pollution, with emission standards that, while considerably more lenient than in other major polluters China and India, are rarely enforced.
The company said that at ground level, its plants mostly comply with South African nitrogen-dioxide emission levels and where they don’t, it’s due to nearby vehicle traffic and other industrial sources.
The two newest of its 14 operating coal-fired plants, Medupi and Kusile, as well as Camden are fitted with so-called low NOx burners to reduce emissions of nitrogen dioxide and others may retrofitted with the equipment, it said. Flue-gas desulfurization units, which slash sulfur-dioxide emissions, are fitted at Medupi and Kusile, it said.
Still, that equipment is currently being bypassed at Kusile after an accident.
Most Read from Bloomberg Businessweek
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
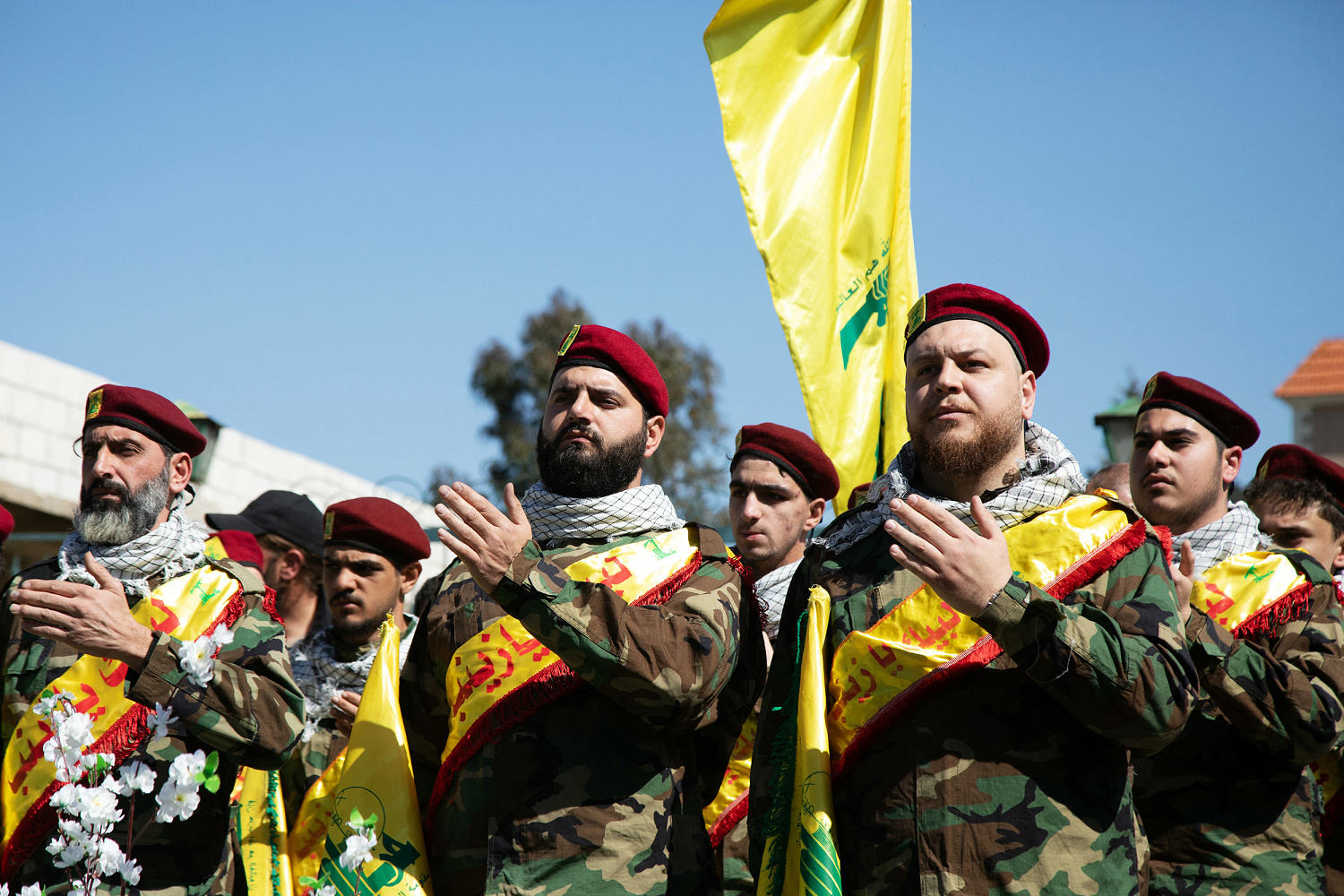

The Syrian army says Israeli airstrikes early Friday near the northern city of Aleppo killed or wounded “a number of” people and caused damage. An opposition war monitor said the strikes killed 42, most of them Syrian troops.
The Britain-based Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, an opposition war monitor, said Israeli strikes hit missile depots for Lebanon’s militant Hezbollah group in Aleppo’s southern suburb of Jibreen, near the Aleppo International Airport, and the nearby town of Safira, home to a sprawling military facility.
The Observatory said 36 Syrian troops and six Hezbollah fighters died, and dozens of people were wounded, calling it the deadliest such attack in years.
There was no immediate statement from Israeli officials on the strikes.
Israel, which has vowed to stop Iranian entrenchment in its northern neighbor, has carried out hundreds of strikes on targets in government-controlled parts of Syria in recent years, but it rarely acknowledges them.
The strikes came less than 24 hours after judges at the International Court of Justice unanimously ordered Israel to take all the necessary and effective action to ensure basic food supplies arrive without delay to the Palestinian population in Gaza.
The ICJ said the Palestinians in Gaza face worsening conditions of life, and famine and starvation are spreading.
“The court observes that Palestinians in Gaza are no longer facing only a risk of famine (…) but that famine is setting in,” the judges said in their order.
The new measures were requested by South Africa as part of its ongoing case that accuses Israel of state-led genocide in Gaza.
In January the ICJ, also known as the World Court, ordered Israel to refrain from any acts that could fall under the Genocide Convention and to ensure its troops commit no genocidal acts against Palestinians in Gaza.
In Thursday’s order the court reaffirmed the January measures but added Israel must take action to ensure unhindered provision of basic services and humanitarian assistance including food, water and electricity as well as medical supplies and medical care to Palestinians throughout Gaza.
The judges added that this could be done “by increasing the capacity and number of land crossing points and maintaining them open for as long as necessary”. The court ordered Israel to submit a report in a month after the order to detail how it had given effect to the ruling.
MANILA, Philippines (AP) — A Filipino villager plans to be nailed to a wooden cross for the 35th time to reenact Jesus Christ’s suffering in a brutal Good Friday tradition he said he would devote to pray for peace in Ukraine, Gaza and the disputed South China Sea.
Ruben Enaje, a 63-year-old carpenter and sign painter, said he and seven other villagers have registered for the real-life crucifixions, which have become an annual religious spectacle that draws hundreds of tourists in three rural communities in Pampanga province north of Manila.
The gory ritual resumed last year after a three-year pause due to the coronavirus pandemic. It has turned Enaje into a village celebrity for his role as the “Christ” in the Lenten reenactment of the Way of the Cross.
Ahead of the crucifixions, Enaje told The Associated Press by telephone Thursday night that he has considered ending his annual religious penitence due to his age but said he could not turn down requests from villagers for him to pray for sick relatives and all other kinds of maladies.
The need for prayers has also deepened in an alarming period of wars and conflicts worldwide, he said.
“If these wars worsen and spread, more people, especially the young and old, would be affected. These are innocent people who have totally nothing to do with these wars,” Enaje said.
Despite the distance, the wars in Ukraine and Gaza have helped send the prices of oil, gas and food soaring elsewhere, including in the Philippines, making it harder for poor people to stretch their meagre income, he said.
Closer to home, the escalating territorial dispute between China and the Philippines in the South China Sea has also sparked worries because it’s obviously a lopsided conflict, Enaje said. “China has many big ships. Can you imagine what they could do?” he asked.
“This is why I always pray for peace in the world,” he said and added he would also seek relief for people in southern Philippine provinces, which have been hit recently by flooding and earthquakes.
In the 1980s, Enaje survived nearly unscathed when he accidentally fell from a three-story building, prompting him to undergo the crucifixion as thanksgiving for what he considered a miracle. He extended the ritual after loved ones recovered from serious illnesses, one after another, and he landed more carpentry and sign-painting job contracts.
During the annual crucifixions on a dusty hill in Enaje’s village of San Pedro Cutud in Pampanga and two other nearby communities, he and other religious devotees, wearing thorny crowns of twigs, carry heavy wooden crosses on their backs for more than a kilometer (more than half a mile) often in the scorching summer heat. Village actors dressed as Roman centurions later hammer 4-inch (10-centimeter) stainless steel nails through their palms and feet, then set them aloft on wooden crosses under the sun for about 10 minutes as a large crowd prays and snaps pictures.
Other penitents walk barefoot through village streets and beat their bare backs with sharp bamboo sticks and pieces of wood. Some participants in the past opened cuts in the penitents’ backs using broken glass to ensure the ritual was sufficiently bloody.
Many of the mostly impoverished penitents undergo the ritual to atone for their sins, pray for the sick or for a better life, and give thanks for miracles.
The gruesome spectacle reflects the Philippines’ unique brand of Catholicism, which merges church traditions with folk superstitions.
Church leaders in the Philippines, the largest Catholic nation in Asia, have frowned on the crucifixions and self-flagellations. Filipinos can show their faith and religious devotion, they say, without hurting themselves and by doing charity work instead, such as donating blood, but the tradition has lasted for decades.
RABAT, Morocco (AP) — Orange blossoms are among Morocco’s quintessential fragrances. Moroccan women are welcoming spring by collecting the waxy white blossoms in copper pots used to distill the scent that’s folded into honey-laden pastries, sprinkled on mint tea and used in religious ceremonies as an ode to paradise.
The annual ceremony in homes across the North African kingdom has attracted international attention. It is now being showcased at the Zahria Festival in Marrakech.
Between 400 and 600 people gathered over the weekend for the festival hosted by Al Muniya Association, celebrating the blooms and savoring the rainfall that is infrequent the rest of the year.
“It’s an old tradition, and it was necessary to give it new life after it was a little bit forgotten in the 1980s and 1990s,” said Jaafar el-Kenousi, the association’s co-founder.
Orange blossoms bloom throughout Morocco but are especially common in Marrakech, home to a particularly fragrant sour and bitter orange tree.
As Morocco’s status grows as a tourist destination, the orange blossom fragrance is increasingly known among visitors and professional perfumers.
The distillation has been recognized as part of Morocco’s heritage by the government and the Islamic World Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. The event now seeks recognition from UNESCO, el-Kenousi said.
Salt bricks and sweeping mud walls – as recently showcased by some African architects – may be the building blocks for innovative designs of the future.
Such ideas were explored by Nigerian architect Tosin Oshinowo in a major exhibition she recently curated in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
She wanted to look at how regions such as Africa are able to function with scarce resources.
“I think ultimately the big elephant in the room for most of us is climate change,” Ms Oshinowo told the BBC about the show The Beauty of Impermanence: An Architecture of Adaptability.
Designers from 26 countries were invited to Sharjah to come up with works to address the issue of scarcity.
For Ethiopian designer Miriam Hillawi Abraham, this meant building what looked like a church out of salt.
She called the work Museum of Artifice – and it was a nod to Ethiopia’s famous rock-hewn churches in Lalibela as well as the remote northern village of Dallol.
This is in the Danakil Depression, more than 330ft (100m) below sea level, and arguably the hottest place on Earth.
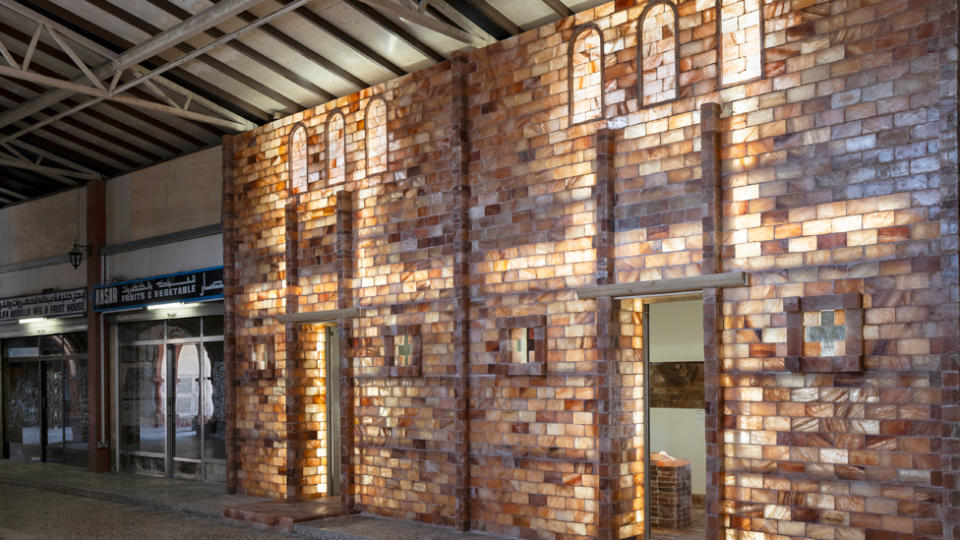

Largely abandoned now, Dallol still has single-storey buildings made out of blocks cut from the nearby salt lakes.
Ms Miriam’s structure, made from pink Himalayan salt, will erode without regular maintenance.
“It does raise the question: ‘What can we learn from these locations?'” Ms Oshinowo said.
Another work at the Sharjah Architecture Triennial was by Hive Earth Studio, a Ghanaian architecture firm that specialises in compressing locally sourced earth to form walls.
It was called Eta’dan, meaning “mud wall” in Ghana’s Fante language – and the soil was sourced in the UAE to reduce the environmental impact of transporting materials.
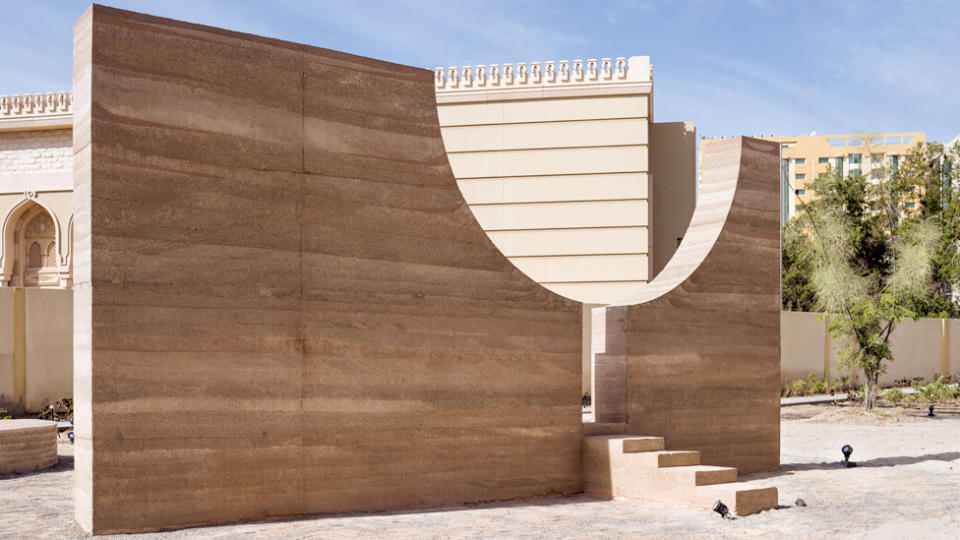

Hive Earth’s ethos is to learn from the past to create buildings for the present, seeking sustainability and a pleasing aesthetic.
Ms Oshinowo said the design team, who had been at the forefront of exploring the technology of rammed earth in West Africa, used rocks from the UAE to achieve the layering and strength required for the walls.
“Through material exploration they were able to transfer the skills of rammed earth,” she said.
“There was a lot of testing to see how it would work in this environment, especially where you have a lot of sand.
“It just shows you what the possibilities are. If we think of things differently, we really can change the way we build and the way we design our buildings.”
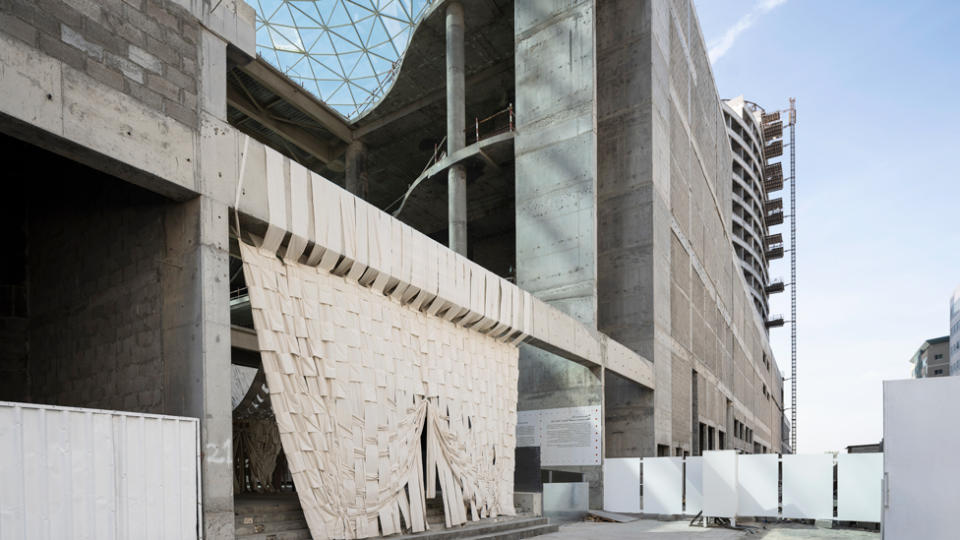

Ghana-based design duo Dominique Petit-Frère and Emil Grip tackled the potential of unfinished building projects – prevalent in West Africa.
Known as Limbo Accra, the pair transformed a derelict shopping mall into an inviting space.
They worked in collaboration with Ivorian fashion label Super Yaya to artfully drape strips of white calico cotton fabric across the entrance.
The work, Super Limbo, was also a nod to Bedouin culture and their desert tents.
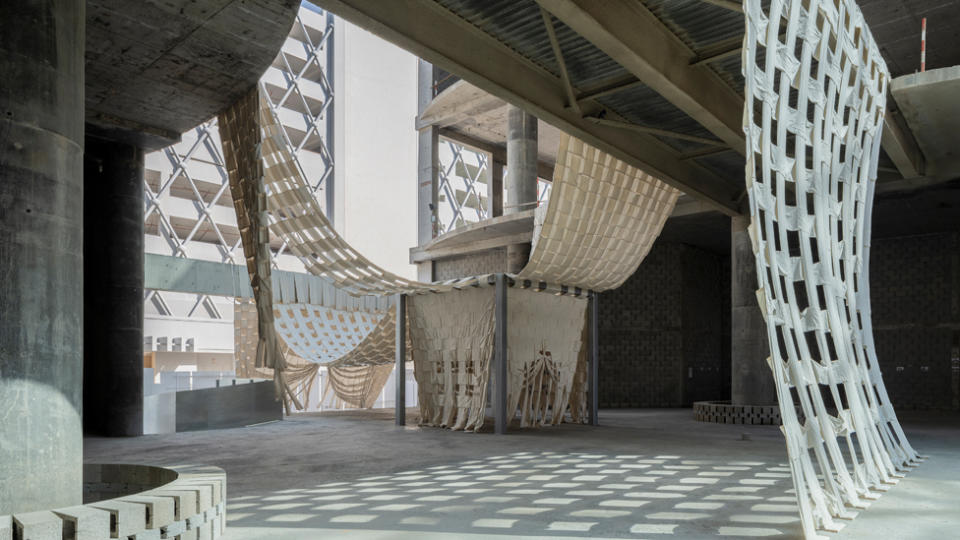

“We were inspired to connect our experiences of navigating the remains of unfinished architecture in West Africa with a Middle Eastern setting,” Ms Petit-Frère told the BBC.
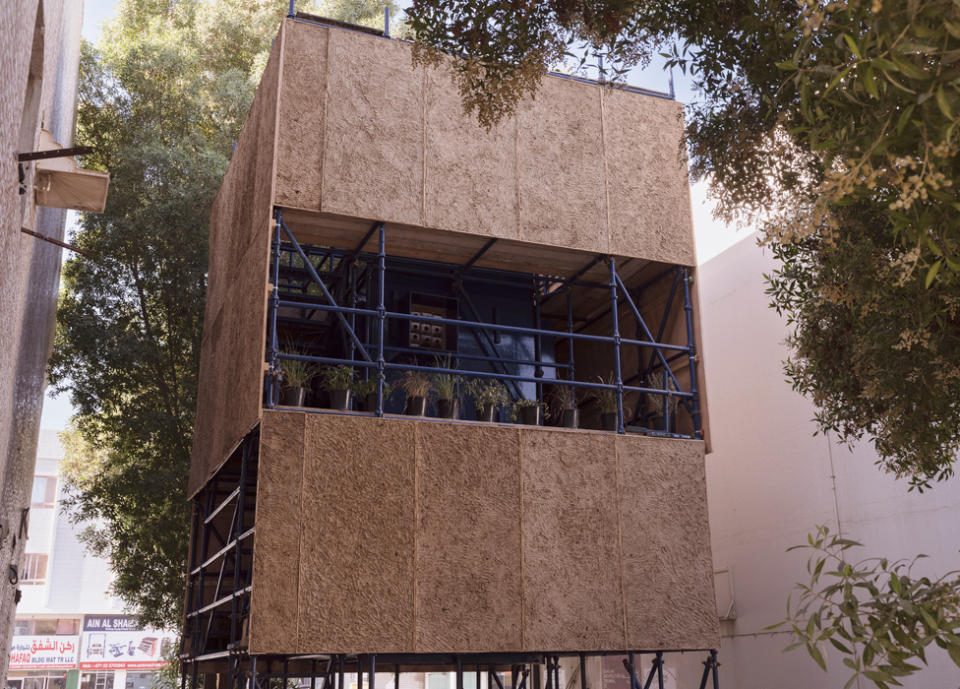
Architects Papa Omotayo and Eve Nnaji, based in the Nigerian city of Lagos, took inspiration from the potted plants and bird cages they spotted being tended by mechanics in an industrial area of Sharjah.
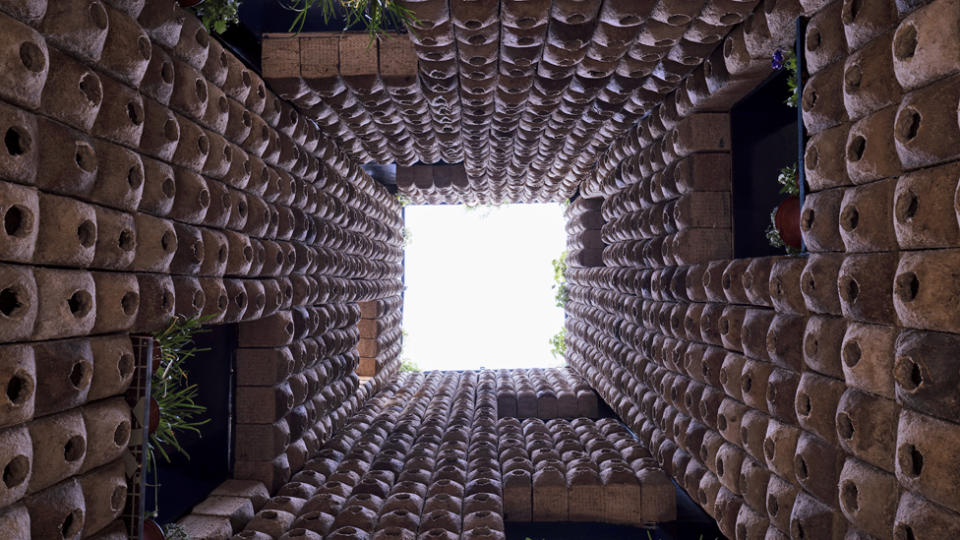
Their three-storey structure We Rest at the Birds Nest was made from scaffolding and organic waste, providing a sanctuary for both birds and workers.
Metal steps led up to platforms decorated with vegetation, while rows of 2,000 biodegradable cardboard nests lined an atrium that descended from the open rooftop to the ground. Passageway windows allowed a view into the birds’ haven.
“As architects we tend to stay focused on people, but we share this planet,” Ms Oshinowo said.
“When we start to think about accommodating other species, it’s also a very powerful narrative.”

Ms Oshinowo hopes the exhibition gave those attending an opportunity to pause and reflect on sustainability and design.
And the exhibits from Africa, a continent disproportionately affected by the climate crisis, showed how designers were starting to work in “better balance with ecology”.
Images subject to copyright.
An AFP photographer captured rare shots showing everyday life in North Korea.
Pedro Pardo accessed a remote part of the border in China’s Jilin province to get the photos.
`The images show a bleak picture of life in the completely isolated nation.
An AFP photographer captured rare images showing daily life in North Korea.
To get the photos, Pedro Pardo accessed a remote part of North Korea’s border with China in the latter’s Jilin province.
The images Pardo took between February 26 and March 1 offer a bleak yet fascinating look at life in a country shrouded in secrecy.
North Korea was founded in 1948 under Kim Il-sung as the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), inspired by strict Marxist-Leninist principles.
Its population of roughly 26 million people lives largely in isolation from the rest of the world in the austere communist state, barred from going abroad without permission from the government and subjected to state-run media that blare propaganda praising the nation and its supreme leader, Kim Jong Un.
North Korea’s self-imposed isolation is largely due to its guiding principle of “juche,” or “self-reliance” — the idea that it should be able to function completely independently and remain separate from the rest of the world.
In practice, this has achieved little other than to stifle the country’s economy and trade, and many of its citizens face high poverty levels and severe food shortages. The CIA says North Korea “remains one of the World’s most isolated and one of Asia’s poorest.”
Since the 1950s, it is estimated that around 31,000 North Koreans have sought to escape and defected to South Korea, The Guardian reported in January.
That number surged last year amid what the unification ministry in Seoul called “worsening conditions in North Korea.”
Pardo’s photos present a unique look into those conditions and life in one of the world’s last communist states.
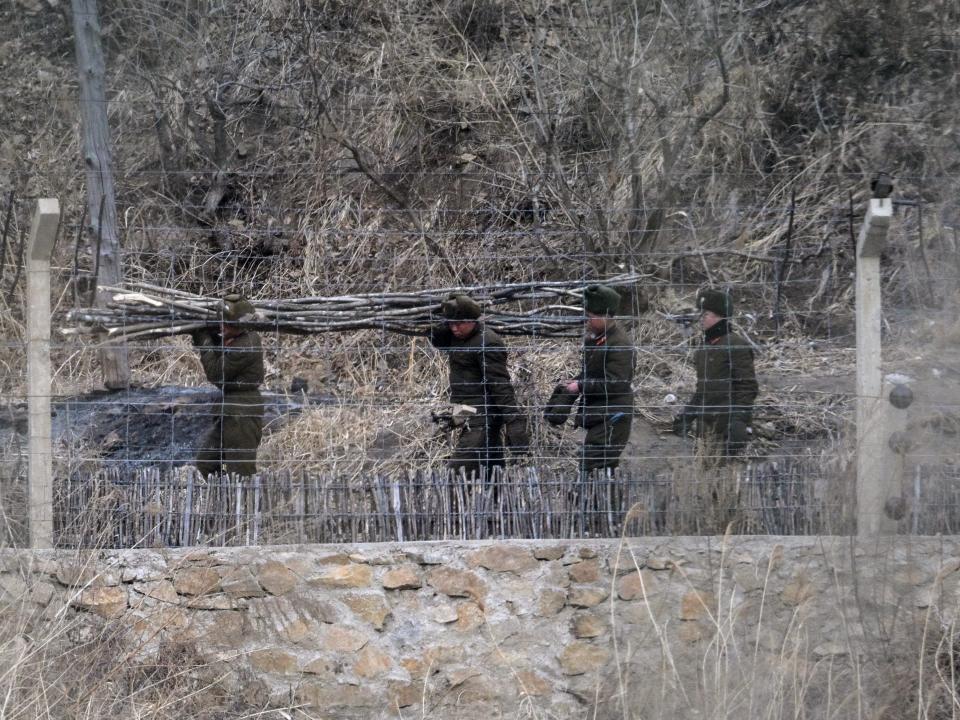
North Korean soldiers working on the border.

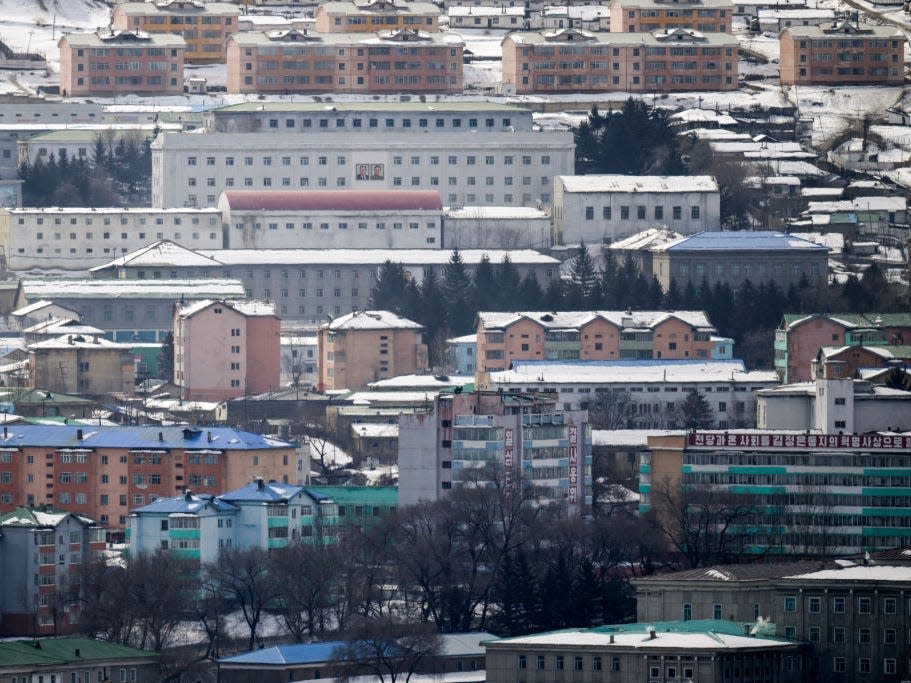
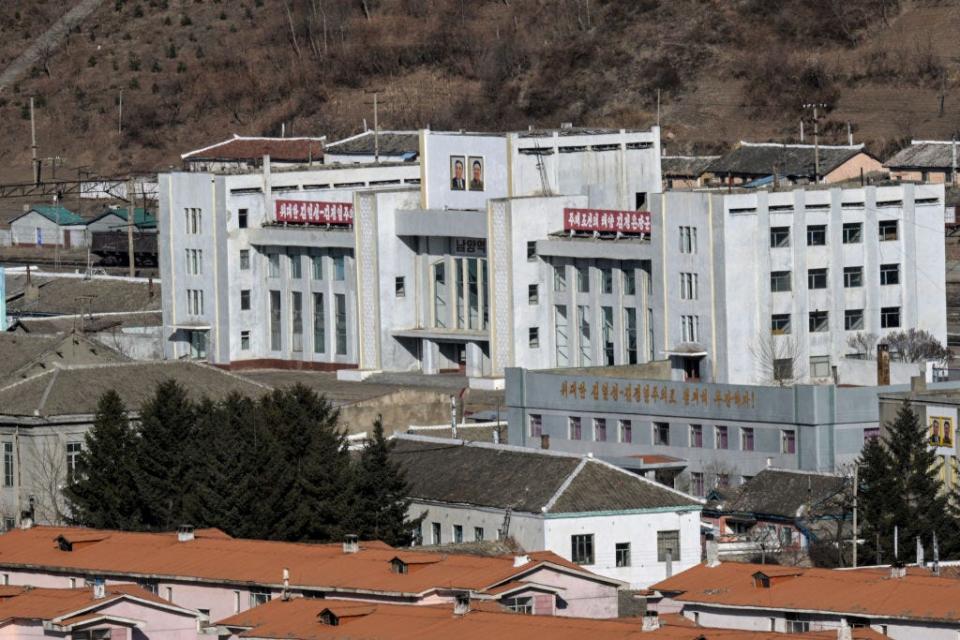
The North Korean city of Hyesan.

A wagon in the North Korean city of Namyang.
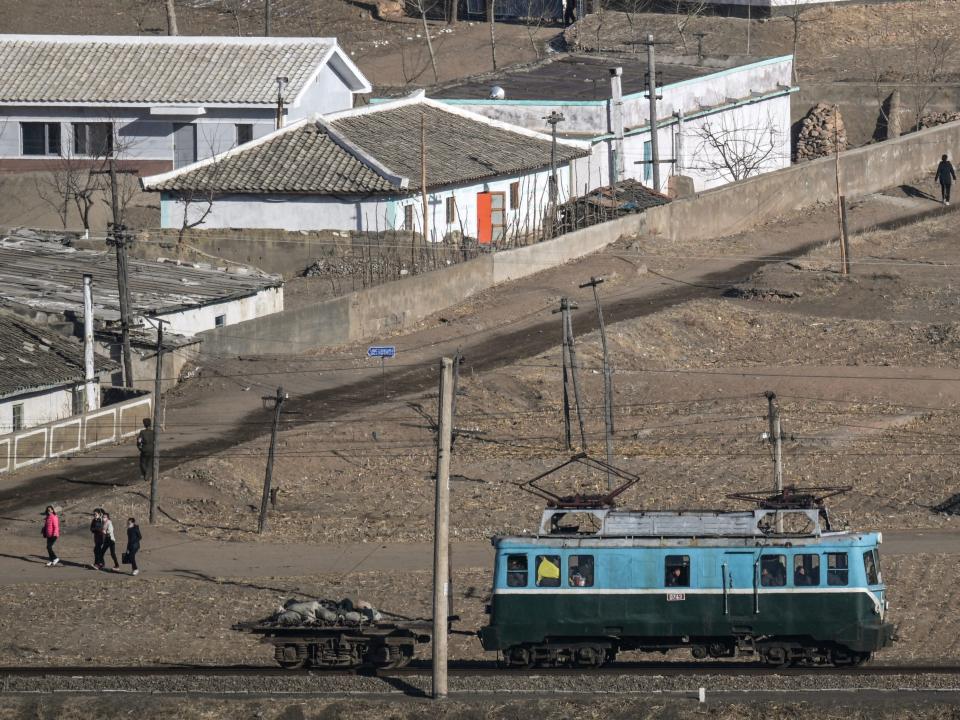
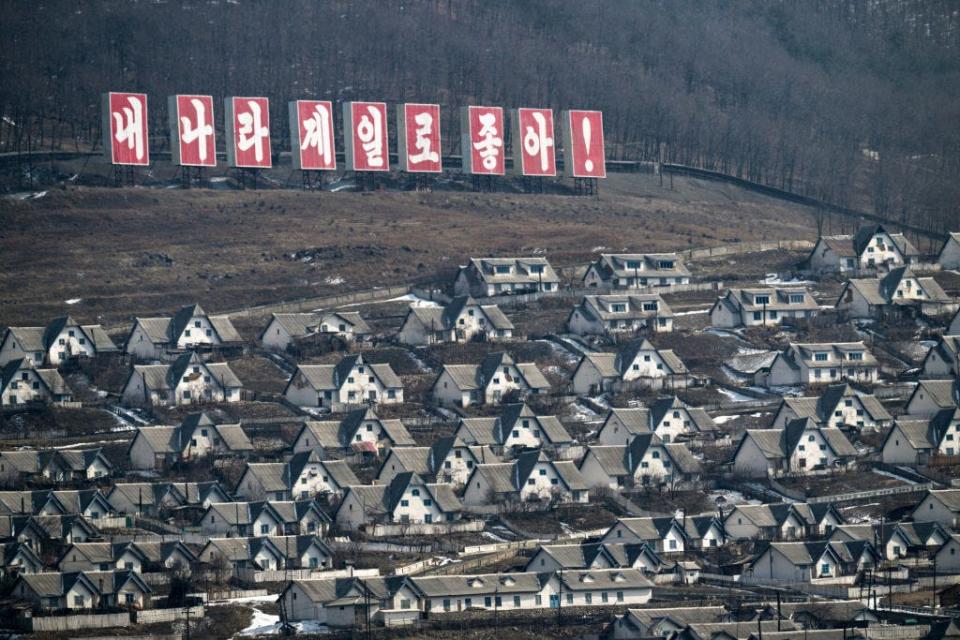
A sign on a hillside in the town of Chunggang reads: “My country is the best.”

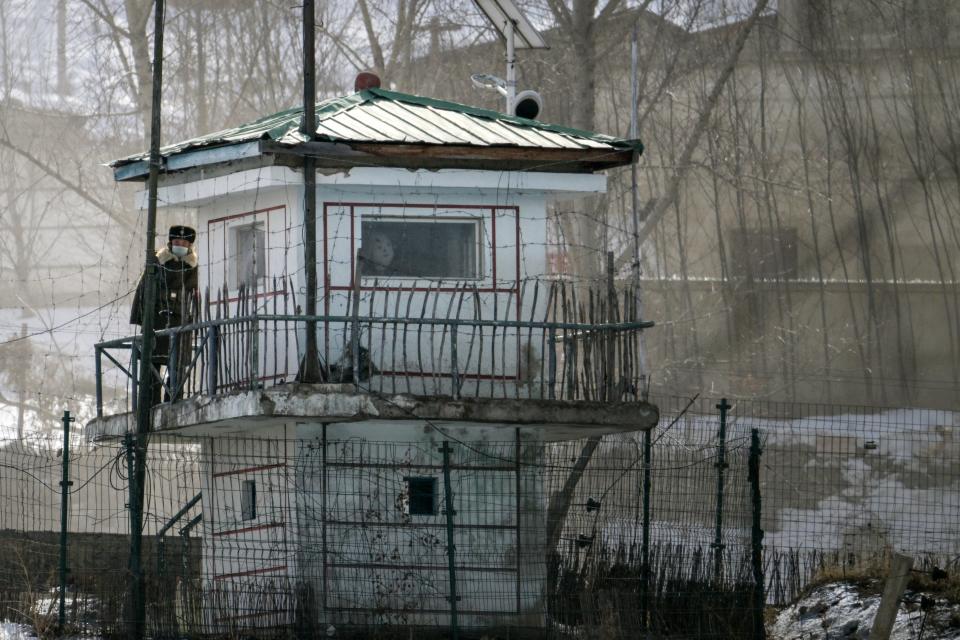
A watchtower by the border in Hyesan.

Portraits of former North Korean leaders Kim Il sung and Kim Jong Il in Chunggang.
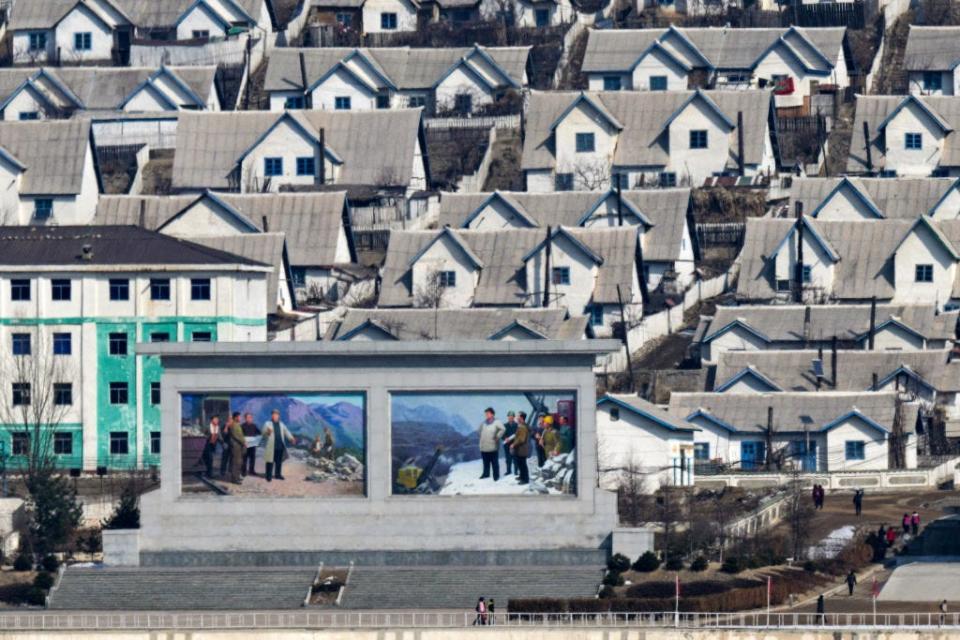

Another set of portraits of the former leaders on a government building in Namyang.

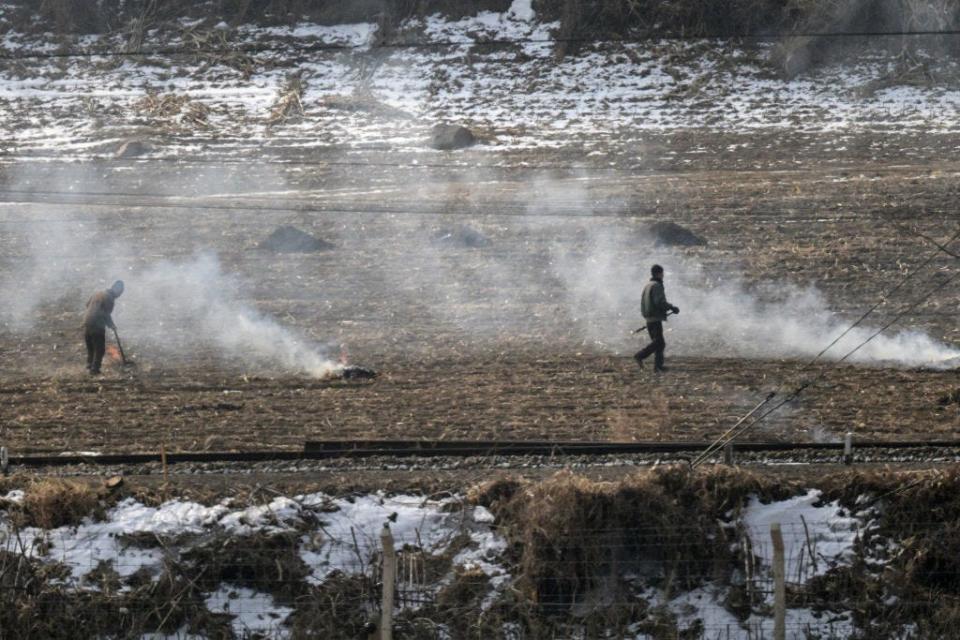
North Korean people working in a field.

A sign in Chunggang reading: “Let’s unify the party and all society with the revolutionary ideas of comrade Kim Jong Un!”

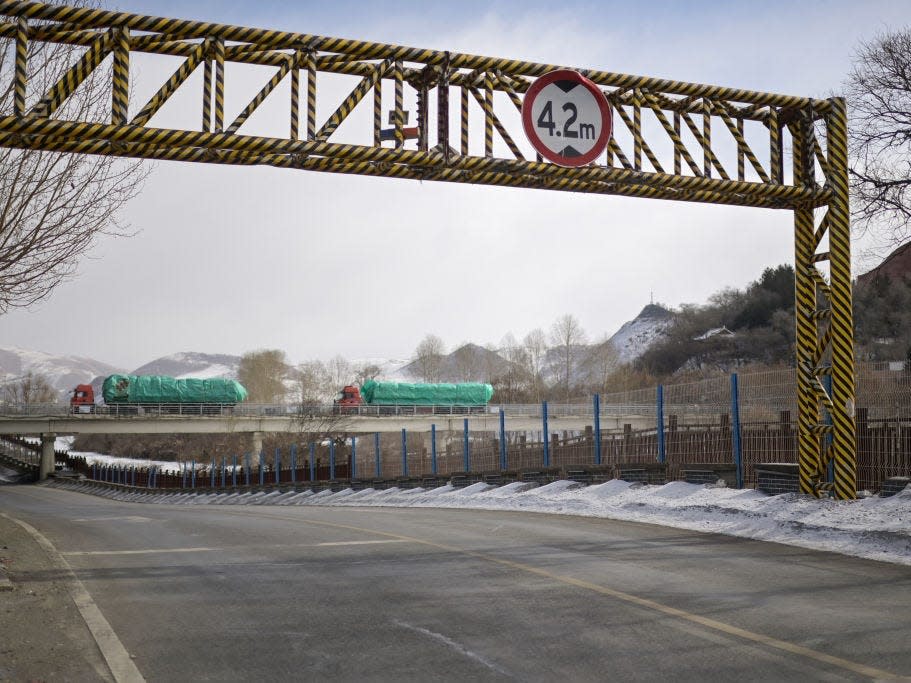
Trucks crossing a border bridge connecting Changbai, China, and Hyesan, North Korea.

Read the original article on Business Insider